Vitamins Guide – VITAMIN K
Vitamin K-Rich Foods for Healthy Blood and Bones
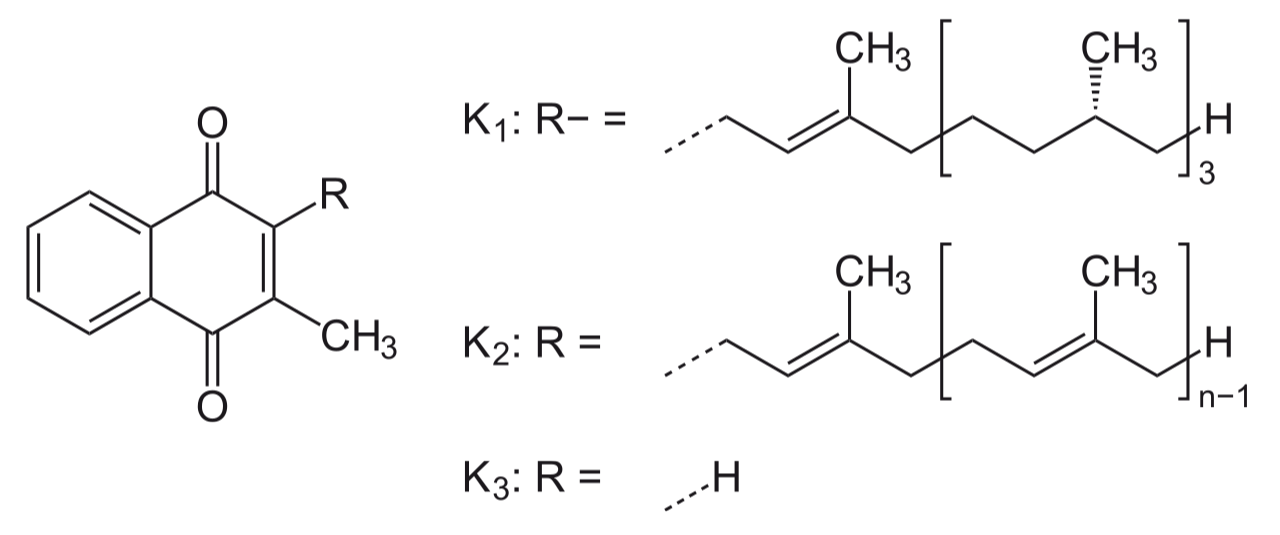
As you can see in the above image, vitamin K comes in three forms. The identifier K for this vitamin is from the German koagulation, which refers to blood clotting as the vitamin is essential for normal blood clotting. It acts as a co-factor for the production of clotting proteins II, VII, IX, X, protein C, and protein S in the liver. The vitamin is also an antidote for the anticoagulant drug warfarin. [1] People taking the warfarin drug should not take vitamin K supplements nor eat a lot of vitamin K-rich foods.
The three active forms of vitamin K are:
Vitamin K RDA
The recommended daily allowance of vitamin K is 90 mcg for women and 120 mcg for men. It is 75 mcg for youngsters. The safe upper level for long-term use is about 1 mg (1,000 mcg).
Vitamin K Benefits
The benefits of eating plenty of vitamin K-rich foods are as follows: -
7 Amazing Vitamin K-Rich Foods
Vitamin K is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in blood clotting and bone health. While it is found in many foods, some are particularly rich in this essential vitamin. Here are the top seven vitamin K-rich foods you can add to your diet for a healthy boost.
But what if you dislike greens?
Well, although not classed as vitamin K-rich foods, the vitamin is present in reasonable amounts in yogurt (from the bacteria), egg yolk, rapeseed, soya, safflower, alfalfa, olive oil, fish liver oils, tomatoes, liver, meat, potatoes, and pulses.
Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Collard Greens

Collard greens are a leafy green vegetable that is not only delicious but also incredibly nutritious. They are a great source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants and have been linked to various health benefits. So whether you’re looking to improve your overall health or simply add some variety to your diet, collard greens are definitely worth considering. Collards come top of the list for vitamin K-rich foods.
Nutritional value of collard greens
Collard greens are a nutritional powerhouse packed with vitamins and minerals essential for good health. One cup of cooked collard greens contains just 49 calories. It provides over 770 mcg per cup or over 600% of the vitamin K RDA, as well as significant amounts of vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium, and iron. They also contain antioxidants like beta-carotene and lutein, which can help protect against chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease.
Ways to incorporate collard greens into your diet
There are many ways to incorporate collard greens into your diet. One popular method is to sauté them with garlic and olive oil for a simple and flavorful side dish. You can also add them to soups, stews, and stir-fries for an extra boost of nutrition. Another option is to use collard greens as a wrap instead of traditional tortillas or bread. Simply blanch the leaves for a few seconds to make them pliable, then fill them with your favorite ingredients. With so many delicious and healthy options, there’s no reason not to add collard greens to your diet.
Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Turnip Greens

If you’re looking for a new superfood to add to your diet, turnip greens may be just what you need. These leafy greens are packed with nutrients and offer a range of health benefits, from improving digestion to reducing inflammation. Turnip greens come second in the list of vitamin K-rich foods.
Nutrient Profile of Turnip Greens
Turnip greens are a nutritional driving force packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. One cup of cooked turnip greens contains 530 mcg or over 400% of the vitamin K RDA, which is essential for bone health and blood clotting. They are also a good source of vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium, and iron. Additionally, turnip greens contain compounds called glucosinolates, which have been shown to have anti-cancer properties.
Ways to Incorporate Turnip Greens into Your Diet
There are many delicious ways to incorporate turnip greens into your diet. A straightforward way is to sauté them with garlic and olive oil for a quick and easy side dish. You can also add them to soups, stews, and stir-fries for an extra boost of nutrition. Another option is to blend them into smoothies or juices for a refreshing and healthy drink. Don't be afraid to get creative and experiment with different recipes to find your favorite way to enjoy turnip greens.
Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Swiss Chard

Swiss chard is a leafy green that is often overlooked, but it is an excellent source of vitamin K – the third in the list of vitamin K-rich foods. One cup of cooked Swiss chard contains 298 mcg or 248% of the vitamin K RDA. It is also a good source of other essential nutrients like vitamins A, C, and magnesium. Swiss chard can be sautéed, added to soups, or used as a base for salads. It is a versatile and delicious leafy green essential for blood clotting and bone health.
Preparing Swiss Chard
To enjoy Swiss chard, try sautéing it with garlic and olive oil, adding it to soups, or using it as a base for salads.
Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Broccoli
Broccoli is a cruciferous vegetable that is high in vitamin K and other important nutrients like vitamin C, fiber, and folate. One cup of cooked broccoli contains 220 mcg or 183% of the vitamin K RDA, and this vegetable is fourth on the list of vitamin K-rich foods. In addition to its high vitamin K content, broccoli is also a great source of vitamin C, which helps boost the immune system and promote healthy skin. It also contains fiber, which can aid digestion and help keep you feeling full.
Preparing broccoli
Broccoli can be prepared in a variety of ways, from simply steaming or roasting it with olive oil and garlic to adding it to soups, salads, and stir-fries. So next time you’re looking for vitamin K-rich food, don’t forget this versatile and nutritious vegetable.
Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Broccoli
Brussels sprouts are a member of the cruciferous vegetable family, just like broccoli, and one of the best vitamin K-rich foods. They are also a great source of vitamin K, with one cup of cooked Brussels sprouts containing 220 mcg or 148% of the RDA. In addition to being high in vitamin K, Brussels sprouts are also packed with other important nutrients like vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants. These nutrients work together to support a healthy immune system, promote healthy digestion, and protect against chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease.
Preparing Brussels sprouts
Roasting or sautéing Brussels sprouts with garlic and olive oil is a delicious way to enjoy this nutritious vegetable. So next time you’re looking for a healthy side dish, consider adding roasted or sautéed Brussels sprouts to your plate. Or, if you don’t cook them or very lightly warm Brussels sprouts up before they begin to stink, you’ll get maximum benefit nutritionally from the vegetable. But, you see, heating Brussels sprouts release smelly sulfur compounds putting many people off from eating this superfood. By not cooking them, they fit salads like lettuce.
Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Spinach
Spinach is another leafy green packed with nutrients, including vitamin K. One cup of cooked spinach contains 145 mcg or 120% of the vitamin K RDA. Spinach is also a great source of other essential nutrients like iron, calcium, and vitamin A. In addition to its high vitamin K content, spinach is an excellent source of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds. These nutrients can help protect against chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. Spinach is also low in calories and high in fiber, making it a great choice for weight management.
Preparing spinach
Add spinach to your salads and omelets, sauté it as a side, add it to your smoothies, or blend it into a pesto for a nutrient-packed boost. Unfortunately, spinach is another green, like broccoli, that develops unpleasant sulfurous tones when cooked. You now know why and the remedy.
Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Kale
Finally, kale is one of the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet. It’s also one of the best sources of vitamin K. Just one cup of raw kale contains 113 mcg or about the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin K. This leafy green is also packed with other essential nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin A, and fiber. Kale is a cruciferous vegetable with numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease and cancer. Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health, and kale is one of the best sources of this important nutrient. In addition to vitamin K, kale is also rich in antioxidants, which help protect against cell damage and inflammation.
Preparing kale
Add kale to your salads or smoothies, or sauté it as a side dish for a delicious and nutritious boost. To get the most out of your kale, try massaging it with a bit of olive oil and lemon juice to soften the leaves and enhance the flavor. You can also bake kale chips for a crunchy and healthy snack.
Vitamin K Supplementation
Most people get enough vitamin K, so there's really no need for its supplementation. Still, supplementing with ALL 16 essential vitamins at the same time is a good idea. Our EV-16 Essential 16 Vitamins give you TWICE the recommended daily allowance of most of these essential vitamins. Below is a complete list of the vitamins in these supplements. Notice that the K vitamin is K1. There is no vitamin K2.
References:
1. Warfarin
See also:
Vitamin A; Vitamin B1; Vitamin B2; Vitamin B3; Vitamin B5; Vitamin B6; Vitamin B7; Vitamin B12; Vitamin C; Vitamin D; Vitamin E; Vitamin K
Synonymous terms: vitamin k rich foods; foods that are rich in vitamin k; list of vitamin k rich foods



